Carbon Dioxide
Does the ice radical (Kangxi radical number 15) bīng 冫 depict a weak intermolecular bond in dry ice?
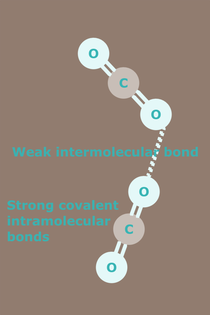
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula CO2), comprises two oxygen atoms bonded to a single carbon atom. The solid form commonly known as dry ice, exists as a molecular solid at temperatures below −78.5 °C. In its solid state, the molecules of carbon dioxide are held together by weak intermolecular bonds. A weak intermolecular bond can exist between two carbon atoms or between two oxygen atoms. Where the bond is between two oxygen atoms, the structure might look something like that in the diagram above.
The crystal structure of dry ice looks something like the diagram below.
Reference
Image Credit: Ben Mills, 2007: Ball-and-stick model of part of the crystal structure of solid carbon dioxide (dry ice), CO2. Crystal structure data from [http://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/AMS/amcsd.php AMCSD]: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Carbon-dioxide-crystal-3D-balls.png

 Cave Script
Translation Project
Cave Script
Translation Project
